
Jest to najstarszy dinozaur pancerny znaleziony w całej Azji i pomaga nam zrozumieć, kiedy i gdzie te zwierzęta pojawiły się po raz pierwszy. Źródło: © Yu Chen
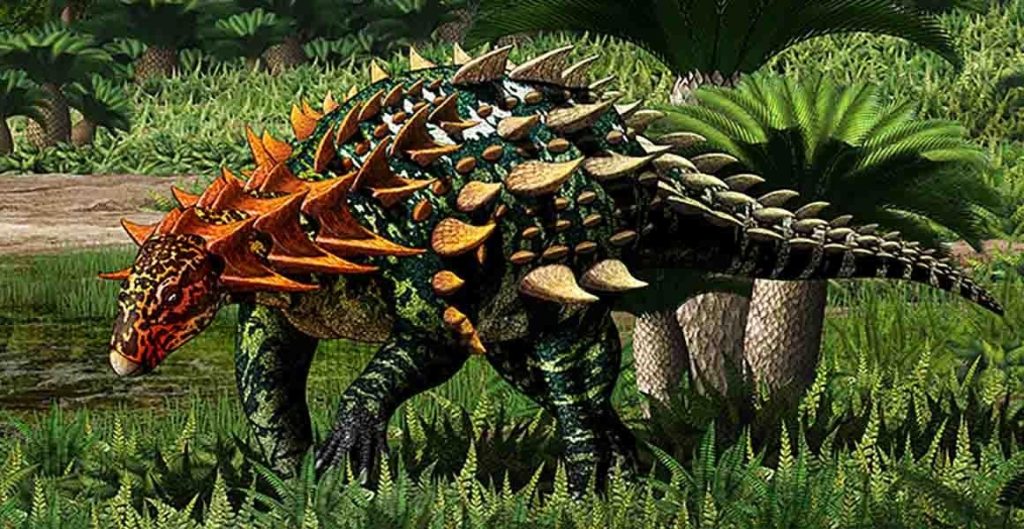
Opisano nowy typ dinozaura pancernego z Chin. Są to najstarsze szczątki skamieniałości z tej grupy znalezione w Azji, co pomaga zrozumieć, w jaki sposób te dziwne dinozaury ewoluowały i rozprzestrzeniały się na całym świecie.
Dinozaury pancerne należą do najsłynniejszych dinozaurów, w tym słynnych zwierząt, takich jak stegozaur A Ankylozaur.
W rzeczywistości jednym z pierwszych dinozaurów, które zostały nazwane, był pancernik, rodzaj ankylozaura odkryty w West Sussex, znany jako Hyleozaur.
To nowe odkrycie zwierzęcia, które żyło na długo przed którymkolwiek z tych dobrze znanych gatunków, pomaga naukowcom zrozumieć, kiedy i gdzie po raz pierwszy pojawiły się opancerzone dinozaury, zanim szybko skolonizowały resztę świata.
Profesor Paul Barrett, badacz dinozaurów w muzeum, który koncentruje się na dinozaurach roślinożernych, pomógł opisać nowy gatunek ze swoimi chińskimi kolegami.
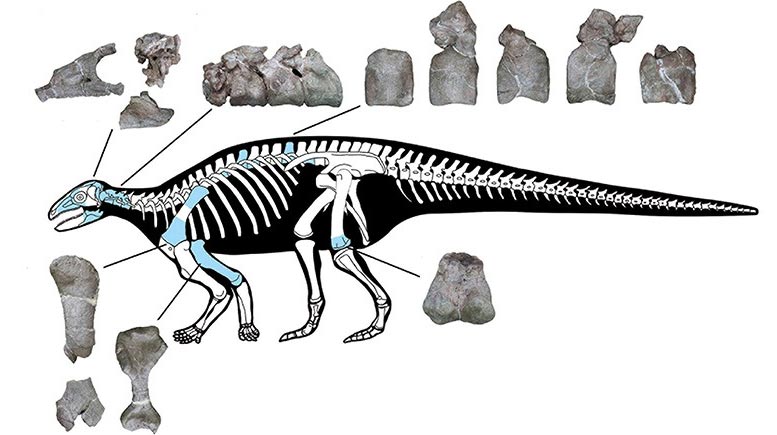
Znalezisko skamieniałości składa się z kompletnego szkieletu, w tym części czaszki, kręgów, części kończyn oraz wielu, wielu zbroi. Jest to najstarszy najlepiej zachowany przykład pancernego dinozaura z całej Azji.
„Tarcza natychmiast mówi nam, że należy do tej samej grupy dinozaurów, co stegozaury i ankylozaury, ale epoka dinozaurów mówi nam, że jest to wczesny członek, wykraczający poza którąkolwiek z tych dwóch grup, a zatem bliski wspólnemu przodek obu”.
Artykuł, który opisuje i nazywa Yuxisaurus kopchicki Został opublikowany w czasopiśmie e-życie.
Pochodzenie dinozaurów pancernych
podczas[{” attribute=””>Jurassic and into the Cretaceous Periods a wealth of herbivorous dinosaurs evolved to be covered in extraordinary defensive bony plates, spikes, and knobs.
These dinosaurs are split into the stegosaurs on one side and the ankylosaurs on the other. The more famous stegosaurs, with their ridge of plates running along their backs and spiked tails, were large bulky animals, while the hulking ankylosaurs were generally covered in flat bony shields and were more like “walking coffee tables.”
Together, the stegosaurs and ankylosaurs are thought to have evolved from a shared ancestor and so form a group known as the thyreophorans, meaning “shield-bearers.” But there have long been questions about when and where this group evolved.
“My colleagues in China discovered this new armored dinosaur in Yunnan, southwest China, in rocks of Early Jurassic age dating to between 192-174 million years ago,” explains Paul. “When we put the animal into an evolutionary analysis, it came out close to the common ancestry of stegosaurs and ankylosaurs.
“This helps to confirm that early armored dinosaurs were living in this region at this time. We know very little about the early history in general of herbivorous dinosaurs in China, so regionally this is a really important discovery.”
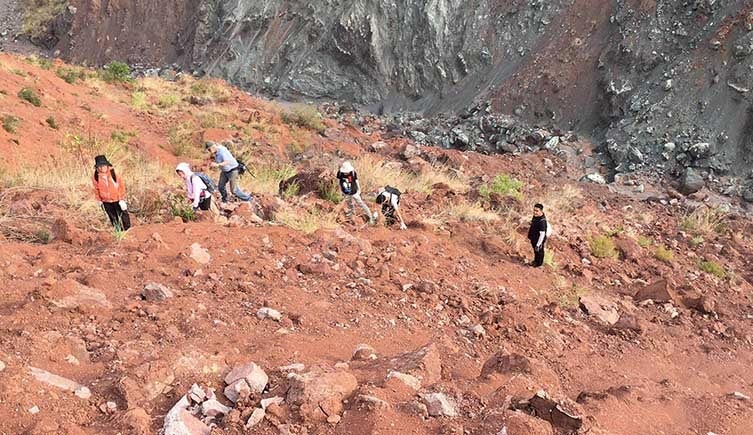

This part of China is rich in dinosaur fossils, but it has largely been dominated by sauropods and their relatives. Credit: ©Shundong Bi
In the past, thyreophoran dinosaurs have largely been associated with the rocks dating to the Late Jurassic and Cretaceous periods (163-66 million years ago) of North America and Europe. This has revealed an incredible diversity of species, but it has long been known that their origins must go much further back.
This historic paucity of finds from the southern continents has led to some suggesting that the group must have evolved in the north. But recent finds are muddying this opinion, with both the earliest known ankylosaur and stegosaur unearthed in the same rock formation in Morocco and dating to around 165 million years ago.
“There are early armored dinosaurs starting to turn up more in the south,” explains Paul. “There are two animals from about 200 million years ago from Venezuela and South Africa, that don’t have armor, but might be the earliest members of the group, showing what they looked like before they evolved armor.
“If these animals were in the group then it is likely the armored dinosaurs originated in the southern continents, but this idea is controversial. If they aren’t included in the group, then the origins are anchored in the northern hemisphere. At the moment, we’ve no way to choose between these alternatives.”

The new find helps to fill out what we know about this part of the world during the Early Jurassic some 192-174 million years ago. Credit: ©Yu Chen
A cosmopolitan dinosaur
This new discovery is not the earliest-known member of this group, but a contemporary of a number of other species from around the world, such as species in Germany and the UK. What this find does do is help to fill in the picture of what this region in China looked like at this moment in time and how these animals were evolving.
This particular formation in China has revealed other dinosaur fossils, but so far it is dominated by the large, long-necked sauropods and their early relatives. This new find adds to the diversity of the other herbivores that must have also been present in the ecosystem at the time.
The fact that Yuxisaurus dates to the Early Jurassic is also of interest. The animal is different from the other early armored dinosaurs as it has a stockier build and a distinctive arrangement of armored plates that would have covered its back. This suggests that these early animals were experimenting with their body shapes and ecology earlier than scientists previously thought.
“The armored dinosaurs appeared at the start of the Jurassic and within a few million years were already evolving into quite a few different types,” explains Paul. “In addition to that they achieved a worldwide distribution very early in their history.
“A bunch of really early members of stegosaurs and ankylosaurs from slightly later in time have been found spread around the world, so they must have been able to move across and between continents.
“Until recently, we assumed that all armored dinosaur evolution happened in the north, but new finds are showing that this was not true.”
Reference: “A new early branching armored dinosaur from the Lower Jurassic of southwestern China” by Xi Yao, Paul M Barrett, Lei Yang, Xing Xu and Shundong Bi, 15 March 2022, eLife.
DOI: 10.7554/eLife.75248







More Stories
Jak czarne dziury stały się tak duże i szybkie? Odpowiedź kryje się w ciemności
Według skamieniałości prehistoryczna krowa morska została zjedzona przez krokodyla i rekina
Wystrzelenie rakiety Falcon 9 firmy SpaceX zostało wstrzymane ze względu na zbliżanie się dwóch głównych misji załogowych lotów kosmicznych